Tools to build a fault-tolerant application
The Hades environment relies on a generic task model called Hades
task model. With this task model, every task is described by
a direct acyclic graph whose nodes model a sequence of code without
synchronization or a system call, and edges model precedence constraints
between them. For each task can be specified a set of synchronization
attributes (e.g. use of resources), timing attributes (e.g.
deadline), distribution attributes (e.g. site to make a computation)
and fault-tolerance attributes (e.g. replication strategy
to use).
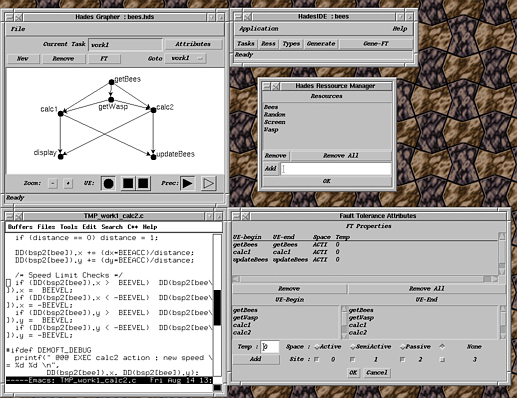
The HadesIDE graphic tool allows to describe the graph and
the attributes of every task. The application designer does not
himself manage fault-tolerance of his applications. The following
figure shows the conception of the work1 task that manages
the moving of critical and non-critical bees.
View larger
version of the HadeIDE off-line tool
work1 is made of six computation nodes (at the top in the
left of the figure) :
-
getBees gets the position of the bees on Hades 1
;
-
getWasp gets the position of the wasp on Hades 0
;
-
cal1 computes the position of the critical bees on Hades
1 (the application designer does not manage replication
for fault-tolerance on Hades 3) ;
-
cal2 computes the position of the non-critical bees
on Hades 2 ;
-
updateBees backups the position of the bees on Hades
1 ;
-
display displays the bees on the screen of Hades
0.
The HadesIDE tool allows the application designer to indicate
which pieces of task graphs to replicate for fault-tolerance, and
which strategies of replication to use (at the bottom in the right
of the previous figure). The available strategies of replication
are active, passive and semi-active replication
to treat site failures and temporal replication to detect
site errors. Each piece of a distributed task can use a different
replication strategy and a different replication degree. On the
example, the application designer has indicated that getBees,
cal1 and updateBees must be replicated on Hades
1 and Hades 3. For this application, the designer has
chosen the active replication.
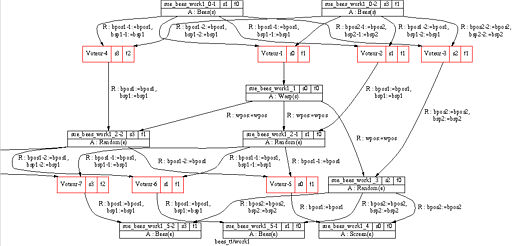
When the conception of an application is terminated, it can be
transformed in a fault-tolerant application thanks to the replication
tool. This tool is in charge of modifying the graph of the application
tasks thanks to various transformation schemes: each transformation
scheme implements a replication strategy. In the following figure,
we present the work1 task after the use of the replication
tool.
View larger
version of the work1 task after replication
A third off-line tool, called sched, implements the scheduling
algorithms. A scheduling algorithm computes on-line or off-line
the execution order of tasks and to verify the respect of their
deadlines. For hard real-time applications, the respect of deadlines
must be verified off-line. The sched tool only implements
the off-line pieces of the scheduling algorithms. For the bees
application, we used a distributed version of the off-line scheduling
algorithm of Xu and Parnas [XuPa90].
A fourth off-line tool computes the memory which is necessary for
an application. This tool also generates the application binary
for the Hades platform.
- [XuPa90]
- J. Xu and D.L. Parnas. Scheduling Processes with Release Times,
Deadlines, Precedence, and Exclusion Relations. IEEE Trans.
on Software Engineering, 16(3):360-369, Mar. 1990.
|